Celebrity News | Interesting updates about the latest celebrity news
Ground Tax In Germany: Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Paying Grundsteuer
Understanding and Paying Ground Tax in Germany: A Comprehensive Guide
Editor's Notes: The need for a comprehensive understanding of ground tax in Germany has prompted the publication of this exhaustive guide today. Ground tax is a crucial aspect of property ownership in Germany, and this guide is designed to equip individuals with the knowledge and resources necessary to make informed decisions.
Our team has meticulously analyzed and compiled extensive information to create this all-encompassing guide, serving as a valuable resource for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of ground tax in Germany.
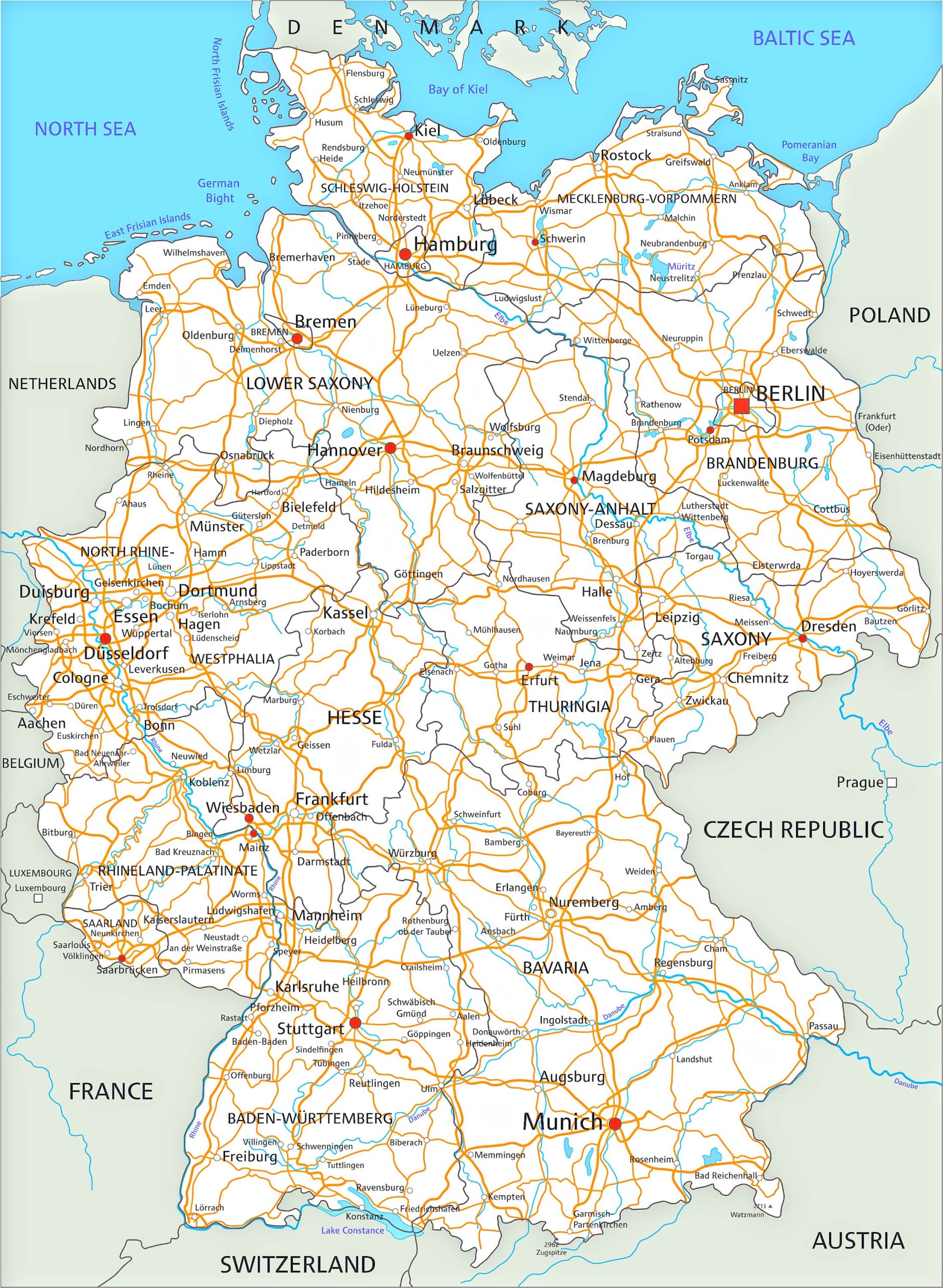
Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Towns And Cities - Source mapspecialist.pages.dev
FAQ
This FAQ section provides comprehensive answers to common questions surrounding ground tax in Germany, known as Grundsteuer. Explore the following Q&A pairs to clarify essential concepts and gain a thorough understanding of your Grundsteuer obligations.
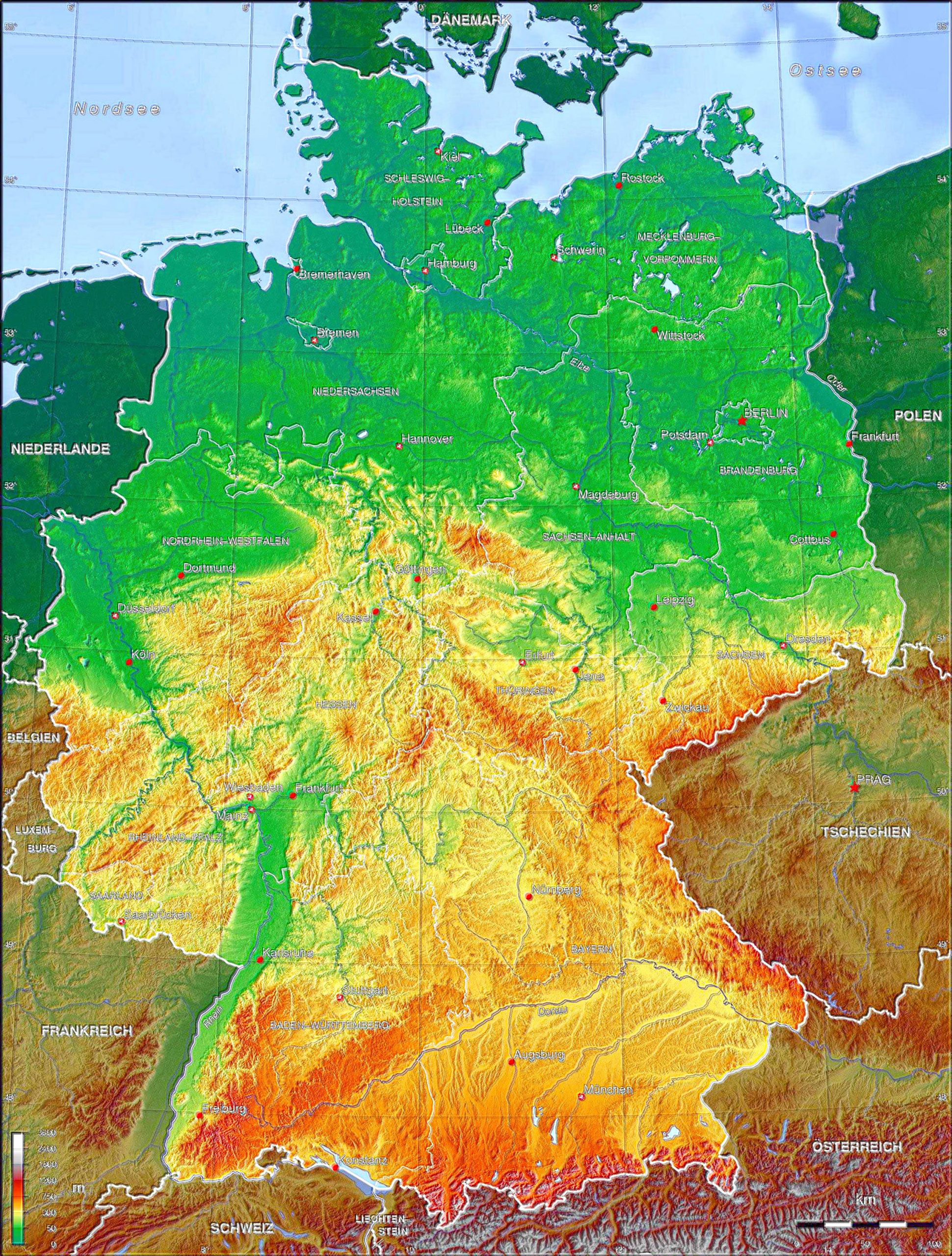
Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Geography And - Source precipitationworldmap.pages.dev
Question 1: What exactly is Grundsteuer?
Answer: Grundsteuer is an annual property tax levied on all owners of land and buildings in Germany. It is calculated based on the assessed value of the property and varies depending on factors such as location, size, and type of property.
Question 2: Who is responsible for paying Grundsteuer?
Answer: The owner of the property as of January 1st of each year is legally responsible for paying Grundsteuer.
Question 3: How is the amount of Grundsteuer determined?
Answer: The amount of Grundsteuer is calculated by multiplying the property's assessed value by the applicable tax rate. Tax rates are set by individual municipalities and can vary significantly.
Question 4: When is Grundsteuer due?
Answer: Grundsteuer is typically due in quarterly installments, with payment deadlines varying depending on the municipality.
Question 5: Are there any exemptions or reductions for Grundsteuer?
Answer: Certain properties may be eligible for exemptions or reductions in Grundsteuer, such as properties used for agricultural purposes or properties owned by non-profit organizations.
Question 6: What are the consequences of not paying Grundsteuer?
Answer: Failure to pay Grundsteuer may result in penalties, interest charges, and even legal action. Therefore, it is essential to pay Grundsteuer on time to avoid any potential consequences.
Understanding and fulfilling your Grundsteuer obligations is crucial as a property owner in Germany. By addressing these common questions, this FAQ aims to provide clarity and guidance, empowering you to navigate the complexities of ground tax effectively.
Proceed to the next article section to delve deeper into the intricacies of calculating Grundsteuer in Germany and explore strategies for optimizing your tax burden.
Tips: Ground Tax In Germany
Getting to understand the nitty-gritty of ground tax in Germany can be a little mind-boggling. But with the right approach, you can navigate the complexities and ensure you meet your tax obligations. Here are a few tips to help you delve into the world of Ground Tax In Germany: Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Paying Grundsteuer.
Tip 1: Determine Your Tax Liability
Understanding who is responsible for paying ground tax is crucial. In Germany, the owner of the property as of January 1st of the tax year is liable for the tax. Even if you acquire the property later in the year, you're still on the hook for the full amount of ground tax for that year.
Tip 2: Calculate Your Tax Amount
Calculating your ground tax bill involves a three-step process: determining the land value, applying the assessment rate, and multiplying the result by the tax rate. The land value is usually based on an official assessment conducted by the local tax authority.
Tip 3: File Your Tax Return
In most cases, you don't have to file a separate ground tax return. The tax authority typically sends out pre-filled tax forms to property owners. These forms usually contain all the necessary information and calculations. You just need to check if everything is correct and submit the form by the deadline.
Tip 4: Pay Your Tax Bill
To avoid late payment penalties and interest charges, make sure to pay your ground tax bill on time. The due dates vary depending on the municipality, so check your tax notice for specific details. You can pay your ground tax online, by bank transfer, or in person at the local tax office.
Tip 5: Seek Professional Help
If you encounter complexities or have questions regarding your ground tax liability, don't hesitate to seek professional advice. A tax consultant or lawyer can provide personalized guidance and help you navigate the intricacies of German ground tax.
Understanding and paying ground tax in Germany can be manageable by following these tips. Remember, staying informed about tax regulations and deadlines is essential to avoid any potential issues.
Ground Tax In Germany: Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Paying Grundsteuer
Comprehending the complexities of Grundsteuer, the property tax levied in Germany, demands a thorough examination of its essential aspects. This guide delves into six key facets of Grundsteuer, providing a comprehensive understanding of its implications for property owners.
- Legal Framework: Understanding the legal basis and regulations governing Grundsteuer.
- Tax Base: Identifying the components that determine the taxable value of a property.
- Tax Rates: Exploring the variables influencing the tax rate applied to a property.
- Exemptions and Reductions: Discovering potential exemptions and reductions that may apply to certain properties.
- Payment Process: Understanding the procedure for paying Grundsteuer, including deadlines and methods.
- Consequences of Non-Payment: Examining the penalties and consequences associated with failing to pay Grundsteuer on time.
Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Geography And - Source precipitationworldmap.pages.dev
These key aspects provide a comprehensive framework for understanding Grundsteuer and navigating the complexities of property taxation in Germany. By delving into each aspect, property owners can gain valuable insights into their tax obligations, ensuring timely payments and avoiding potential penalties.
Ground Tax In Germany: Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Paying Grundsteuer
Ground tax (Grundsteuer) is a property tax levied on owners of land and buildings in Germany. It is a municipal tax, meaning that it is collected by the local authorities. The amount of ground tax owed is calculated based on the value of the property and the tax rate set by the municipality.
Navigating Germany: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Geography And - Source precipitationworldmap.pages.dev
Ground tax is an important source of revenue for municipalities in Germany. It is used to fund a variety of local services, such as schools, roads, and parks. The amount of ground tax owed can vary significantly from one municipality to another, depending on the local tax rate.
There are a number of exemptions and deductions that can be applied to ground tax. For example, owners of owner-occupied homes are entitled to a basic exemption of €500. There are also exemptions for certain types of property, such as agricultural land and forest land.
Ground tax is payable in two installments, on January 1 and July 1. If the tax is not paid on time, the municipality may impose penalties.
Ground tax is a complex topic, and it is important to understand the rules and regulations that apply to your specific situation. If you have any questions about ground tax, you should contact your local tax office.